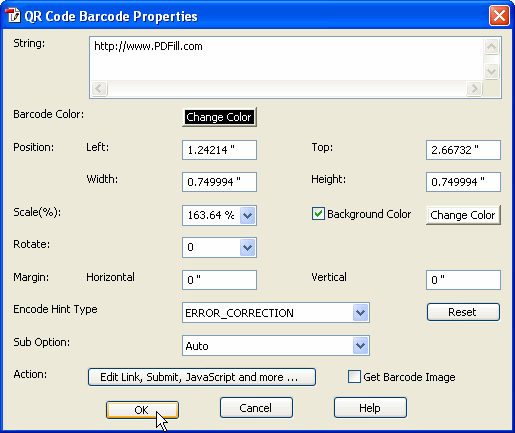
The QR Code system became popular outside the automotive industry due to its fast readability and greater storage capacity compared to standard UPC barcodes. Applications include product tracking, item identification, time tracking, document management, and general marketing.[2]
QR Code (abbreviated
from Quick Response Code) is the trademark for a type
of
matrix barcode (or two-dimensional
barcode) first designed for the
automotive industry in Japan. A barcode is a
machine-readable optical label that contains information
about the item to which it is attached. A QR code uses four
standardized encoding modes (numeric, alphanumeric, byte /
binary, and
kanji) to efficiently store data; extensions may also be
used.[1]